Introduction
Understanding verb forms is essential for mastering English grammar. These forms help express actions in different times and contexts, allowing us to communicate effectively. This article will explore four key verb forms: Simple Present, Simple Past, Present Perfect, and Present Continuous. Examples using common verbs like “eat,” “write,” “text,” “chat,” and others will illustrate how these forms work in real-life situations. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of these verb forms and their applications.
1. Simple Present Tense
The Simple Present tense describes habitual actions, general truths, and facts. It is one of the most commonly used verb forms in English.
Formula:
Subject + Base Verb (add -s or -es for third-person singular)
Examples:
- Eat: I eat breakfast every morning.
- Write: She writes in her journal daily.
- Text: They text their friends frequently.
- Chat: He chats with his colleagues during breaks.
- Look: We look at the stars every night.
- Watch: She watches the news every evening.
- Lead: He leads the team effectively.
- Drive: They drive to work every day.
- Open: I open the windows every morning.
- Check: She checks her emails regularly.
- Travel: We travel to new places every summer.
- Watch: He watches documentaries on weekends.
Explanation:
- Simple Present emphasises regular habits (e.g., “I eat breakfast every morning”).
- It also conveys facts and truths (e.g., “She writes in her journal daily”).
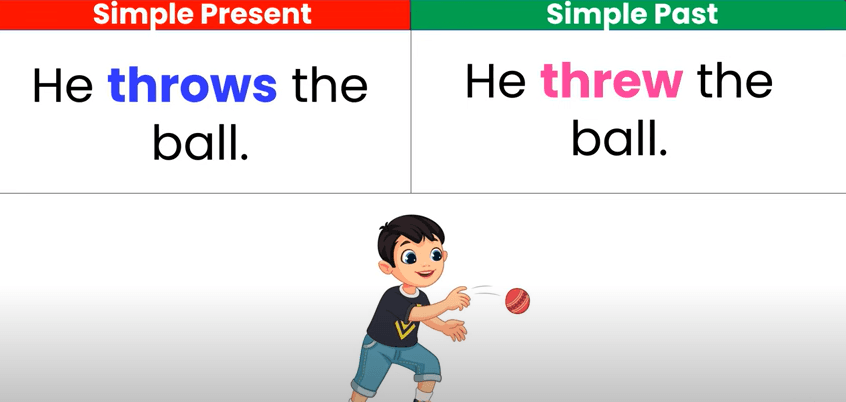
2. Simple Past Tense
The Simple Past tense is used to describe actions that were completed in the past. This verb form is vital for storytelling and recounting events.
Formula:
Subject + Past Form of the Verb
Examples:
- Eat: I ate pizza for dinner last night.
- Write: She wrote a letter to her friend yesterday.
- Text: They texted their parents about their plans.
- Chat: He chatted with his neighbour this morning.
- Look: We looked at the photos from our trip.
- Watch: She watched a movie last weekend.
- Lead: He led the team to victory.
- Drive: They drove to the beach on Saturday.
- Open: I opened the door when the bell rang.
- Check: She checked her schedule before the meeting.
- Travel: We travelled to Europe last summer.
- Watch: He watched the sunrise from the hill.
Explanation:
- Simple Past refers to actions completed at a specific time in the past (e.g., “I ate pizza for dinner last night”).
- It is essential for narrating events (e.g., “They drove to the beach on Saturday”).
3. Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect tense connects past actions to the present. It is one of the more nuanced verb forms, often used to show experience or ongoing relevance.
Formula:
Subject + Have/Has + Past Participle
Examples:
- Eat: I have eaten sushi many times.
- Write: She has written three books so far.
- Text: They have texted the group about the changes.
- Chat: He has chatted with the manager about his concerns.
- Look: We have looked everywhere for the missing keys.
- Watch: She has watched that series multiple times.
- Lead: He has led several successful projects.
- Drive: They have driven across the country twice.
- Open: I have opened all the boxes but found nothing.
- Check: She has checked her messages already.
- Travel: We have travelled to many exotic destinations.
- Watch: He has watched the entire season in one day.
Explanation:
- Present Perfect links past actions to the present (e.g., “I have eaten sushi many times”).
- It highlights experience or ongoing relevance (e.g., “She has written three books so far”).
4. Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous tense describes actions happening right now or ongoing activities. This verb form is often used with time expressions like “now” or “currently.”
Formula:
Subject + Am/Is/Are + Verb + -ing
Examples:
- Eat: I am eating lunch right now.
- Write: She is writing a new novel.
- Text: They are texting their friends at the moment.
- Chat: He is chatting with his family online.
- Look: We are looking for a new apartment.
- Watch: She is watching a live concert on TV.
- Lead: He is leading a meeting currently.
- Drive: They are driving to the airport as we speak.
- Open: I am opening the package now.
- Check: She is checking her calendar for available dates.
- Travel: We are travelling to Asia next week.
- Watch: He is watching a tutorial to learn guitar.
Explanation:
- Present Continuous emphasizes actions happening now (e.g., “I am eating lunch right now”).
- It also describes ongoing activities (e.g., “She is writing a new novel”).
Comparing the Four Verb Forms
To better understand the differences between these verb forms, let’s use the verb “travel” in each tense:
- Simple Present: I travel to new places every summer.
- Simple Past: I travelled to Japan last year.
- Present Perfect: I have travelled to over 10 countries.
- Present Continuous: I am travelling to Italy next month.
Key Differences:
- Simple Present focuses on routine or general truths.
- Simple Past emphasizes completed actions.
- Present Perfect links past actions to the present.
- Present Continuous highlights actions happening at the moment.
Practical Applications
Daily Conversations:
Understanding these verb forms helps in everyday interactions. For example:
- “I eat breakfast every morning” (habit).
- “I ate breakfast earlier” (past event).
- “I have eaten breakfast already” (experience).
- “I am eating breakfast right now” (current action).
Writing:
When writing stories, reports, or essays, using the correct verb forms ensures clarity and accuracy.
- Example for storytelling: “She wrote a letter, and she has never forgotten the response.”
Professional Settings:
Clear use of verb forms is crucial in professional communication. For instance:
- “I have completed the report” (Present Perfect) conveys the task’s completion and relevance.
Practice Makes Perfect
To master these verb forms, practice is essential. Try creating sentences using the following verbs in each form:
- Eat: Simple Present, Simple Past, Present Perfect, Present Continuous.
- Write: Apply the same pattern.
- Travel: Practice with different contexts.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering verb forms like Simple Present, Simple Past, Present Perfect, and Present Continuous is key to effective communication in English. By practising these tenses with common verbs like “eat,” “write,” “text,” “chat,” and others, you can build confidence in both speaking and writing. Keep practising, and soon these tenses will become second nature! allowing us to communicate effectively. This article will explore four key verb forms: Simple Present, Simple Past, Present Perfect, and Present Continuous. Examples using common verbs like “eat,” “write,” “text,” “chat,” and others will illustrate how these forms work in real-life situations. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of these verb forms and their applications.
1. Simple Present Tense
The Simple Present tense describes habitual actions, general truths, and facts. It is one of the most commonly used verb forms in English.
Formula:
Subject + Base Verb (add -s or -es for third-person singular)
Examples:
- Eat: I eat breakfast every morning.
- Write: She writes in her journal daily.
- Text: They text their friends frequently.
- Chat: He chats with his colleagues during breaks.
- Look: We look at the stars every night.
- Watch: She watches the news every evening.
- Lead: He leads the team effectively.
- Drive: They drive to work every day.
- Open: I open the windows every morning.
- Check: She checks her emails regularly.
- Travel: We travel to new places every summer.
- Watch: He watches documentaries on weekends.
Explanation:
- Simple Present emphasises regular habits (e.g., “I eat breakfast every morning”).
- It also conveys facts and truths (e.g., “She writes in her journal daily”).
2. Simple Past Tense
The Simple Past tense is used to describe actions that were completed in the past. This verb form is vital for storytelling and recounting events.
Formula:
Subject + Past Form of the Verb
Examples:
- Eat: I ate pizza for dinner last night.
- Write: She wrote a letter to her friend yesterday.
- Text: They texted their parents about their plans.
- Chat: He chatted with his neighbour this morning.
- Look: We looked at the photos from our trip.
- Watch: She watched a movie last weekend.
- Lead: He led the team to victory.
- Drive: They drove to the beach on Saturday.
- Open: I opened the door when the bell rang.
- Check: She checked her schedule before the meeting.
- Travel: We travelled to Europe last summer.
- Watch: He watched the sunrise from the hill.
Explanation:
- Simple Past refers to actions completed at a specific time in the past (e.g., “I ate pizza for dinner last night”).
- It is essential for narrating events (e.g., “They drove to the beach on Saturday”).
3. Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect tense connects past actions to the present. It is one of the more nuanced verb forms, often used to show experience or ongoing relevance.
Formula:
Subject + Have/Has + Past Participle
Examples:
- Eat: I have eaten sushi many times.
- Write: She has written three books so far.
- Text: They have texted the group about the changes.
- Chat: He has chatted with the manager about his concerns.
- Look: We have looked everywhere for the missing keys.
- Watch: She has watched that series multiple times.
- Lead: He has led several successful projects.
- Drive: They have driven across the country twice.
- Open: I have opened all the boxes but found nothing.
- Check: She has checked her messages already.
- Travel: We have travelled to many exotic destinations.
- Watch: He has watched the entire season in one day.
Explanation:
- Present Perfect links past actions to the present (e.g., “I have eaten sushi many times”).
- It highlights experience or ongoing relevance (e.g., “She has written three books so far”).
4. Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous tense describes actions happening right now or ongoing activities. This verb form is often used with time expressions like “now” or “currently.”
Formula:
Subject + Am/Is/Are + Verb + -ing
Examples:
- Eat: I am eating lunch right now.
- Write: She is writing a new novel.
- Text: They are texting their friends at the moment.
- Chat: He is chatting with his family online.
- Look: We are looking for a new apartment.
- Watch: She is watching a live concert on TV.
- Lead: He is leading a meeting currently.
- Drive: They are driving to the airport as we speak.
- Open: I am opening the package now.
- Check: She is checking her calendar for available dates.
- Travel: We are travelling to Asia next week.
- Watch: He is watching a tutorial to learn guitar.
Explanation:
- Present Continuous emphasizes actions happening now (e.g., “I am eating lunch right now”).
- It also describes ongoing activities (e.g., “She is writing a new novel”).
Comparing the Four Verb Forms
To better understand the differences between these verb forms, let’s use the verb “travel” in each tense:
- Simple Present: I travel to new places every summer.
- Simple Past: I travelled to Japan last year.
- Present Perfect: I have travelled to over 10 countries.
- Present Continuous: I am travelling to Italy next month.
Key Differences:
- Simple Present focuses on routine or general truths.
- Simple Past emphasizes completed actions.
- Present Perfect links past actions to the present.
- Present Continuous highlights actions happening at the moment.
Practical Applications
Daily Conversations:
Understanding these verb forms helps in everyday interactions. For example:
- “I eat breakfast every morning” (habit).
- “I ate breakfast earlier” (past event).
- “I have eaten breakfast already” (experience).
- “I am eating breakfast right now” (current action).
Writing:
When writing stories, reports, or essays, using the correct verb forms ensures clarity and accuracy.
- Example for storytelling: “She wrote a letter, and she has never forgotten the response.”
Professional Settings:
Clear use of verb forms is crucial in professional communication. For instance:
- “I have completed the report” (Present Perfect) conveys the task’s completion and relevance.
Practice Makes Perfect
To master these verb forms, practice is essential. Try creating sentences using the following verbs in each form:
- Eat: Simple Present, Simple Past, Present Perfect, Present Continuous.
- Write: Apply the same pattern.
- Travel: Practice with different contexts.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering verb forms like Simple Present, Simple Past, Present Perfect, and Present Continuous is key to effective communication in English. By practising these tenses with common verbs like “eat,” “write,” “text,” “chat,” and others, you can build confidence in both speaking and writing. Keep practising, and soon these tenses will become second nature!

